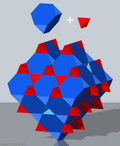
Quarter cubic honeycomb
| Quarter cubic honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| |
| Type | Uniform honeycomb |
| Family | Truncated simplectic honeycomb Quarter hypercubic honeycomb |
| Indexing[1] | J25,33, A13 W10, G6 |
| Schläfli symbol | t0,1{3[4]} or q{4,3,4} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | Template:CDD = Template:CDD = Template:CDD |
| Cell types | {3,3} (3.6.6) |
| Face types | {3}, {6} |
| Vertex figure |  (isosceles triangular antiprism) |
| Space group | FdTemplate:Overlinem (227) |
| Coxeter group | ×22, [[3[4]]] |
| Dual | oblate cubille Cell:  (1/4 of rhombic dodecahedron) |
| Properties | vertex-transitive, edge-transitive |
The quarter cubic honeycomb, quarter cubic cellulation or bitruncated alternated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of tetrahedra and truncated tetrahedra in a ratio of 1:1. It is called "quarter-cubic" because its symmetry unit – the minimal block from which the pattern is developed by reflections – is four times that of the cubic honeycomb.
It is vertex-transitive with 6 truncated tetrahedra and 2 tetrahedra around each vertex.
It is one of the 28 convex uniform honeycombs.
The faces of this honeycomb's cells form four families of parallel planes, each with a 3.6.3.6 tiling.
Its vertex figure is an isosceles antiprism: two equilateral triangles joined by six isosceles triangles.
John Horton Conway calls this honeycomb a truncated tetrahedrille, and its dual oblate cubille.
The vertices and edges represent a Kagome lattice in three dimensions,[2] which is the pyrochlore lattice.
Construction
The quarter cubic honeycomb can be constructed in slab layers of truncated tetrahedra and tetrahedral cells, seen as two trihexagonal tilings. Two tetrahedra are stacked by a vertex and a central inversion. In each trihexagonal tiling, half of the triangles belong to tetrahedra, and half belong to truncated tetrahedra. These slab layers must be stacked with tetrahedra triangles to truncated tetrahedral triangles to construct the uniform quarter cubic honeycomb. Slab layers of hexagonal prisms and triangular prisms can be alternated for elongated honeycombs, but these are also not uniform.

|
 trihexagonal tiling: Template:CDD |
Symmetry
Cells can be shown in two different symmetries. The reflection generated form represented by its Coxeter-Dynkin diagram has two colors of truncated cuboctahedra. The symmetry can be doubled by relating the pairs of ringed and unringed nodes of the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, which can be shown with one colored tetrahedral and truncated tetrahedral cells.
| Symmetry | , [3[4]] | ×2, [[3[4]]] |
|---|---|---|
| Space group | FTemplate:Overline3m (216) | FdTemplate:Overlinem (227) |
| Coloring | 
|

|
| Vertex figure | 
|

|
| Vertex figure symmetry |
C3v [3] (*33) order 6 |
D3d [2+,6] (2*3) order 12 |
Related polyhedra
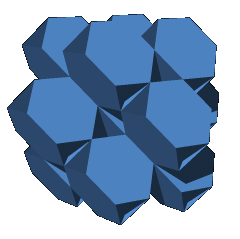 The subset of hexagonal faces of this honeycomb contains a regular skew apeirohedron {6,6|3}. |
 Four sets of parallel planes of trihexagonal tilings exist throughout this honeycomb. |
This honeycomb is one of five distinct uniform honeycombs[3] constructed by the Coxeter group. The symmetry can be multiplied by the symmetry of rings in the Coxeter–Dynkin diagrams:
| A3 honeycombs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space group |
Fibrifold | Square symmetry |
Extended symmetry |
Extended diagram |
Extended group |
Honeycomb diagrams |
| FTemplate:Overline3m (216) |
1o:2 | a1 |
[3[4]] | Template:CDD | (None) | |
| FmTemplate:Overlinem (225) |
2−:2 | d2 |
<[3[4]]> ↔ [4,31,1] |
Template:CDD ↔ Template:CDD |
×21 ↔ |
Template:CDD 1,Template:CDD 2 |
| FdTemplate:Overlinem (227) |
2+:2 | g2 |
Template:Brackets or [2+[3[4]]] |
Template:CDD ↔ Template:CDD |
×22 | Template:CDD 3 |
| PmTemplate:Overlinem (221) |
4−:2 | d4 |
<2[3[4]]> ↔ [4,3,4] |
Template:CDD ↔ Template:CDD |
×41 ↔ |
Template:CDD 4 |
| ITemplate:Overline (204) |
8−o | r8 |
[4[3[4]]]+ ↔ Template:Brackets |
Template:CDD ↔ Template:CDD |
½×8 ↔ ½×2 |
Template:CDD (*) |
| ImTemplate:Overlinem (229) |
8o:2 | [4[3[4]]] ↔ Template:Brackets |
×8 ↔ ×2 |
Template:CDD 5 | ||
The Quarter cubic honeycomb is related to a matrix of 3-dimensional honeycombs: q{2p,4,2q} Template:Quarter hyperbolic honeycomb table
See also
- Truncated simplectic honeycomb
- Triakis truncated tetrahedral honeycomb
- Architectonic and catoptric tessellation
References
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, (2008) The Symmetries of Things, Template:Isbn (Chapter 21, Naming the Archimedean and Catalan polyhedra and tilings, Architectonic and Catoptric tessellations, p 292-298, includes all the nonprismatic forms)
- George Olshevsky, Uniform Panoploid Tetracombs, Manuscript (2006) (Complete list of 11 convex uniform tilings, 28 convex uniform honeycombs, and 143 convex uniform tetracombs)
- Branko Grünbaum, Uniform tilings of 3-space. Geombinatorics 4(1994), 49 - 56.
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- Template:The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure (book)
- Template:Cite book
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, Template:Isbn [1]
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10] (1.9 Uniform space-fillings)
- A. Andreini, Sulle reti di poliedri regolari e semiregolari e sulle corrispondenti reti correlative (On the regular and semiregular nets of polyhedra and on the corresponding correlative nets), Mem. Società Italiana della Scienze, Ser.3, 14 (1905) 75–129.
- D. M. Y. Sommerville, An Introduction to the Geometry of n Dimensions. New York, E. P. Dutton, 1930. 196 pp. (Dover Publications edition, 1958) Chapter X: The Regular Polytopes
- Template:KlitzingPolytopes
- Uniform Honeycombs in 3-Space: 15-Batatoh
| Template:Navbar-collapsible | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space | Family | / / | ||||
| E2 | Uniform tiling | 0[3] | δ3 | hδ3 | qδ3 | Hexagonal |
| E3 | Uniform convex honeycomb | 0[4] | δ4 | hδ4 | qδ4 | |
| E4 | Uniform 4-honeycomb | 0[5] | δ5 | hδ5 | qδ5 | 24-cell honeycomb |
| E5 | Uniform 5-honeycomb | 0[6] | δ6 | hδ6 | qδ6 | |
| E6 | Uniform 6-honeycomb | 0[7] | δ7 | hδ7 | qδ7 | 222 |
| E7 | Uniform 7-honeycomb | 0[8] | δ8 | hδ8 | qδ8 | 133 • 331 |
| E8 | Uniform 8-honeycomb | 0[9] | δ9 | hδ9 | qδ9 | 152 • 251 • 521 |
| E9 | Uniform 9-honeycomb | 0[10] | δ10 | hδ10 | qδ10 | |
| E10 | Uniform 10-honeycomb | 0[11] | δ11 | hδ11 | qδ11 | |
| En-1 | Uniform (n-1)-honeycomb | 0[n] | δn | hδn | qδn | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 |
- ↑ For cross-referencing, they are given with list indices from Andreini (1-22), Williams(1-2,9-19), Johnson (11-19, 21-25, 31-34, 41-49, 51-52, 61-65), and Grünbaum(1-28).
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ [2], Template:OEIS el 6-1 cases, skipping one with zero marks