Kovasznay flow
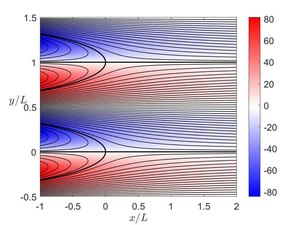
Kovasznay flow corresponds to an exact solution of the Navier–Stokes equations and are interpreted to describe the flow behind a two-dimensional grid. The flow is named after Leslie Stephen George Kovasznay, who discovered this solution in 1948.[1] The solution is often used to validate numerical codes solving two-dimensional Navier-Stokes equations.
Flow description
Let be the free stream velocity and let be the spacing between a two-dimensional grid. The velocity field of the Kovaszany flow, expressed in the Cartesian coordinate system is given by[2]
where is the root of the equation in which represents the Reynolds number of the flow. The root that describes the flow behind the two-dimensional grid is found to be
The corresponding vorticity field and the stream function are given by
Similar exact solutions, extending Kovasznay's, has been noted by Lin and Tobak[3] and C. Y. Wang.[4][5]