Goldberg polyhedron
 Template:Math |
 Template:Math |
 Template:Math |
 Template:Math |
 Template:Math, equilateral and spherical | |
In mathematics, and more specifically in polyhedral combinatorics, a Goldberg polyhedron is a convex polyhedron made from hexagons and pentagons. They were first described in 1937 by Michael Goldberg (1902–1990). They are defined by three properties: each face is either a pentagon or hexagon, exactly three faces meet at each vertex, and they have rotational icosahedral symmetry. They are not necessarily mirror-symmetric; e.g. Template:Math and Template:Math are enantiomorphs of each other. A Goldberg polyhedron is a dual polyhedron of a geodesic polyhedron.
A consequence of Euler's polyhedron formula is that a Goldberg polyhedron always has exactly 12 pentagonal faces. Icosahedral symmetry ensures that the pentagons are always regular and that there are always 12 of them. If the vertices are not constrained to a sphere, the polyhedron can be constructed with planar equilateral (but not in general equiangular) faces.
Simple examples of Goldberg polyhedra include the dodecahedron and truncated icosahedron. Other forms can be described by taking a chess knight move from one pentagon to the next: first take Template:Mvar steps in one direction, then turn 60° to the left and take Template:Mvar steps. Such a polyhedron is denoted Template:Math A dodecahedron is Template:Math, and a truncated icosahedron is Template:Math
A similar technique can be applied to construct polyhedra with tetrahedral symmetry and octahedral symmetry. These polyhedra will have triangles or squares rather than pentagons. These variations are given Roman numeral subscripts denoting the number of sides on the non-hexagon faces: Template:Math Template:Math and Template:Math
Elements
The number of vertices, edges, and faces of GP(m,n) can be computed from m and n, with T = m2 + mn + n2 = (m + n)2 − mn, depending on one of three symmetry systems:[1] The number of non-hexagonal faces can be determined using the Euler characteristic, as demonstrated here.
| Symmetry | Icosahedral | Octahedral | Tetrahedral |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Dodecahedron GPV(1,0) = {5+,3}1,0 |
Cube GPIV(1,0) = {4+,3}1,0 |
Tetrahedron GPIII(1,0) = {3+,3}1,0 |
| Image | |||
| Symbol | GPV(m,n) = {5+,3}m,n | GPIV(m,n) = {4+,3}m,n | GPIII(m,n) = {3+,3}m,n |
| Vertices | |||
| Edges | |||
| Faces | |||
| Faces by type | 12 {5} and 10(T − 1) {6} | 6 {4} and 4(T − 1) {6} | 4 {3} and 2(T − 1) {6} |
Construction
Most Goldberg polyhedra can be constructed using Conway polyhedron notation starting with (T)etrahedron, (C)ube, and (D)odecahedron seeds. The chamfer operator, c, replaces all edges by hexagons, transforming GP(m,n) to GP(2m,2n), with a T multiplier of 4. The truncated kis operator, y = tk, generates GP(3,0), transforming GP(m,n) to GP(3m,3n), with a T multiplier of 9.
For class 2 forms, the dual kis operator, z = dk, transforms GP(a,0) into GP(a,a), with a T multiplier of 3. For class 3 forms, the whirl operator, w, generates GP(2,1), with a T multiplier of 7. A clockwise and counterclockwise whirl generator, wTemplate:Overline = wrw generates GP(7,0) in class 1. In general, a whirl can transform a GP(a,b) into GP(a + 3b,2ab) for a > b and the same chiral direction. If chiral directions are reversed, GP(a,b) becomes GP(2a + 3b,a − 2b) if a ≥ 2b, and GP(3a + b,2b − a) if a < 2b.
Class I
| Frequency | (1,0) | (2,0) | (3,0) | (4,0) | (5,0) | (6,0) | (7,0) | (8,0) | (m,0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 1 | 4 | 9 | 16 | 25 | 36 | 49 | 64 | m2 |
| Icosahedral (Goldberg) | regular dodecahedron |
 chamfered dodecahedron |
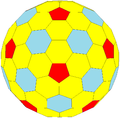
|

|

|
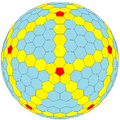
|

|

|
more |
| Octahedral | cube |
 chamfered cube |

|
more | |||||
| Tetrahedral | tetrahedron |
 chamfered tetrahedron |
more |
Class II
| Frequency | (1,1) | (2,2) | (3,3) | (4,4) | (5,5) | (6,6) | (7,7) | (8,8) | (m,m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 3 | 12 | 27 | 48 | 75 | 108 | 147 | 192 | 3m2 |
| Icosahedral (Goldberg) | 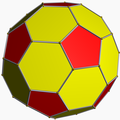 truncated icosahedron |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
more |
| Octahedral |  truncated octahedron |

|
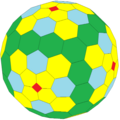
|

|

|
more | |||
| Tetrahedral |  truncated tetrahedron |

|
more |
Class III
| Frequency | (1,2) | (1,3) | (2,3) | (1,4) | (2,4) | (3,4) | (5,1) | (m,n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | 7 | 13 | 19 | 21 | 28 | 37 | 31 | m2+mn+n2 |
| Icosahedral (Goldberg) | 
|
|

|
|

|

|

|
more |
| Octahedral | 
|
more | ||||||
| Tetrahedral | 
|
more |
See also
- Capsid
- Geodesic sphere
- Fullerene#Other buckyballs
- Conway polyhedron notation
- Goldberg–Coxeter construction
Notes
References
- Template:Cite journal
- Joseph D. Clinton, Clinton’s Equal Central Angle Conjecture
- Template:Cite book [1]
- Template:Cite web
- Template:Cite journal
External links
- Dual Geodesic Icosahedra
- Goldberg variations: New shapes for molecular cages Flat hexagons and pentagons come together in new twist on old polyhedral, by Dana Mackenzie, February 14, 2014
- ↑ Clinton’s Equal Central Angle Conjecture, JOSEPH D. CLINTON