Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere
Template:Short description Template:Use dmy dates Template:Use American English

In Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide is a trace gas that plays an integral part in the greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, photosynthesis and oceanic carbon cycle. It is one of three main greenhouse gases in the atmosphere of Earth. The concentration of carbon dioxide (Template:CO2) in the atmosphere reached 427 ppm (0.0427%) on a molar basis in 2024, representing 3341 gigatonnes of Template:CO2.[1] This is an increase of 50% since the start of the Industrial Revolution, up from 280 ppm during the 10,000 years prior to the mid-18th century.[2][3][4] The increase is due to human activity.[5]
The current increase in Template:CO2 concentrations is primarily driven by the burning of fossil fuels.[6] Other significant human activities that emit Template:CO2 include cement production, deforestation, and biomass burning. The increase in atmospheric concentrations of Template:CO2 and other long-lived greenhouse gases such as methane increase the absorption and emission of infrared radiation by the atmosphere. This has led to a rise in average global temperature and ocean acidification. Another direct effect is the [[CO2 fertilization effect|Template:CO2 fertilization effect]]. The increase in atmospheric concentrations of Template:CO2 causes a range of further effects of climate change on the environment and human living conditions.
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. It absorbs and emits infrared radiation at its two infrared-active vibrational frequencies. The two wavelengths are 4.26 μm (2,347 cm−1) (asymmetric stretching vibrational mode) and 14.99 μm (667 cm−1) (bending vibrational mode). Template:CO2 plays a significant role in influencing Earth's surface temperature through the greenhouse effect.[7] Light emission from the Earth's surface is most intense in the infrared region between 200 and 2500 cm−1,[8] as opposed to light emission from the much hotter Sun which is most intense in the visible region. Absorption of infrared light at the vibrational frequencies of atmospheric Template:CO2 traps energy near the surface, warming the surface of Earth and its lower atmosphere. Less energy reaches the upper atmosphere, which is therefore cooler because of this absorption.[9]
The present atmospheric concentration of Template:CO2 is the highest for 14 million years.[10] Concentrations of Template:CO2 in the atmosphere were as high as 4,000 ppm during the Cambrian period about 500 million years ago, and as low as 180 ppm during the Quaternary glaciation of the last two million years.[2] Reconstructed temperature records for the last 420 million years indicate that atmospheric Template:CO2 concentrations peaked at approximately 2,000 ppm. This peak happened during the Devonian period (400 million years ago). Another peak occurred in the Triassic period (220–200 million years ago).[11]
Current concentration and future trends
Current situation
Since the start of the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric Template:Co2 concentration have been increasing, causing global warming and ocean acidification.[12] In October 2023 the average level of Template:CO2 in Earth's atmosphere, adjusted for seasonal variation, was 422.17 parts per million by volume (ppm).[13] Figures are published monthly by the National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).[14][15] The value had been about 280 ppm during the 10,000 years up to the mid-18th century.[2][3][4]
Each part per million of Template:Co2 in the atmosphere represents approximately 2.13 gigatonnes of carbon, or 7.82 gigatonnes of Template:CO2.[16]
It was pointed out in 2021 that "the current rates of increase of the concentration of the major greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide) are unprecedented over at least the last 800,000 years".[17]Template:Rp
Template:As of it is estimated that 2,650 gigatonnes of Template:CO2 have been emitted by human activity since 1850, with annual emissions of 42 gigatonnes per year. About 1,050 gigatonnes remain in the atmosphere following absorption by oceans and land.[18]
Some fraction (a projected 20–35%) of the fossil carbon transferred thus far will persist in the atmosphere as elevated Template:CO2 levels for many thousands of years after these carbon transfer activities begin to subside.[19][20]
Annual and regional fluctuations
Atmospheric Template:CO2 concentrations fluctuate slightly with the seasons, falling during the Northern Hemisphere spring and summer as plants consume the gas and rising during northern autumn and winter as plants go dormant or die and decay. The level drops by about 6 or 7 ppm (about 50 Gt) from May to September during the Northern Hemisphere's growing season, and then goes up by about 8 or 9 ppm. The Northern Hemisphere dominates the annual cycle of Template:CO2 concentration because it has much greater land area and plant biomass in mid-latitudes (30-60 degrees) than the Southern Hemisphere. Concentrations reach a peak in May as the Northern Hemisphere spring greenup begins, and decline to a minimum in October, near the end of the growing season.[21][22]
Concentrations also vary on a regional basis, most strongly near the ground with much smaller variations aloft. In urban areas concentrations are generally higher[23] and indoors they can reach 10 times background levels.
Measurements and predictions made in the recent past
- Data from 2009 found that the global mean Template:CO2 concentration was rising at a rate of approximately 2 ppm/year and accelerating.[24][25]
- The daily average concentration of atmospheric Template:Co2 at Mauna Loa Observatory first exceeded 400 ppm on 10 May 2013[26][27] although this concentration had already been reached in the Arctic in June 2012.[28] Data from 2013 showed that the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is this high "for the first time in 55 years of measurement—and probably more than 3 million years of Earth history."[29]
- As of 2018, Template:CO2 concentrations were measured to be 410 ppm.[24][30]
Measurement techniques

The concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are expressed as parts per million by volume (abbreviated as ppmv, or ppm(v), or just ppm). To convert from the usual ppmv units to ppm mass (abbreviated as ppmm, or ppm(m)), multiply by the ratio of the molar mass of CO2 to that of air, i.e. times 1.52 (44.01 divided by 28.96).
The first reproducibly accurate measurements of atmospheric CO2 were from flask sample measurements made by Dave Keeling at Caltech in the 1950s.[31] Measurements at Mauna Loa have been ongoing since 1958. Additionally, measurements are also made at many other sites around the world. Many measurement sites are part of larger global networks. Global network data are often made publicly available.
Data networks
There are several surface measurement (including flasks and continuous in situ) networks including NOAA/ERSL,[32] WDCGG,[33] and RAMCES.[34] The NOAA/ESRL Baseline Observatory Network, and the Scripps Institution of Oceanography Network[35] data are hosted at the CDIAC at ORNL. The World Data Centre for Greenhouse Gases (WDCGG), part of GAW, data are hosted by the JMA. The Reseau Atmospherique de Mesure des Composes an Effet de Serre database (RAMCES) is part of IPSL.
From these measurements, further products are made which integrate data from the various sources. These products also address issues such as data discontinuity and sparseness. GLOBALVIEW-Template:CO2 is one of these products.[36]
Analytical methods to investigate sources of CO2
- The burning of long-buried fossil fuels releases Template:CO2 containing carbon of different isotopic ratios to those of living plants, enabling distinction between natural and human-caused contributions to Template:CO2 concentration.[37]
- There are higher atmospheric Template:CO2 concentrations in the Northern Hemisphere, where most of the world's population lives (and emissions originate from), compared to the southern hemisphere. This difference has increased as anthropogenic emissions have increased.[38]
- Atmospheric OTemplate:Sub levels are decreasing in Earth's atmosphere as it reacts with the carbon in fossil fuels to form Template:CO2.[39]
Causes of the current increase
Template:Anchor Anthropogenic CO2 emissions
While Template:CO2 absorption and release is always happening as a result of natural processes, the recent rise in Template:CO2 levels in the atmosphere is known to be mainly due to human (anthropogenic) activity.[17] Anthropogenic carbon emissions exceed the amount that can be taken up or balanced out by natural sinks.[41] Thus carbon dioxide has gradually accumulated in the atmosphere and, as of May 2022, its concentration is 50% above pre-industrial levels.[3]
The extraction and burning of fossil fuels, releasing carbon that has been underground for many millions of years, has increased the atmospheric concentration of Template:CO2.[4][12] As of year 2019 the extraction and burning of geologic fossil carbon by humans releases over 30 gigatonnes of Template:CO2 (9 billion tonnes carbon) each year.[42] This larger disruption to the natural balance is responsible for recent growth in the atmospheric Template:CO2 concentration.[30][43] Currently about half of the carbon dioxide released from the burning of fossil fuels is not absorbed by vegetation and the oceans and remains in the atmosphere.[44]
Burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas is the leading cause of increased anthropogenic Template:CO2; deforestation is the second major cause. In 2010, 9.14 gigatonnes of carbon (GtC, equivalent to 33.5 gigatonnes of Template:CO2 or about 4.3 ppm in Earth's atmosphere) were released from fossil fuels and cement production worldwide, compared to 6.15 GtC in 1990.[45] In addition, land use change contributed 0.87 GtC in 2010, compared to 1.45 GtC in 1990.[45] In the period 1751 to 1900, about 12 GtC were released as Template:CO2 to the atmosphere from burning of fossil fuels, whereas from 1901 to 2013 the figure was about 380 GtC.[46]
The International Energy Agency estimates that the top 1% of emitters globally each had carbon footprints of over 50 tonnes of Template:CO2 in 2021, more than 1,000 times greater than those of the bottom 1% of emitters. The global average energy-related carbon footprint is around 4.7 tonnes of Template:CO2 per person.[47]
Roles in natural processes on Earth
Greenhouse effect



On Earth, carbon dioxide is the most relevant, direct greenhouse gas that is influenced by human activities. Water is responsible for most (about 36–70%) of the total greenhouse effect, and the role of water vapor as a greenhouse gas depends on temperature. Carbon dioxide is often mentioned in the context of its increased influence as a greenhouse gas since the pre-industrial (1750) era. In 2013, the increase in CO2 was estimated to be responsible for 1.82 W m−2 of the 2.63 W m−2 change in radiative forcing on Earth (about 70%).[48]
Earth's natural greenhouse effect makes life as we know it possible, and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere plays a significant role in providing for the relatively high temperature on Earth. The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary atmosphere warms the planet's surface beyond the temperature it would have in the absence of its atmosphere.[49][50][51]
The concept of more atmospheric CO2 increasing ground temperature was first published by Svante Arrhenius in 1896.[52] The increased radiative forcing due to increased CO2 in the Earth's atmosphere is based on the physical properties of CO2 and the non-saturated absorption windows where CO2 absorbs outgoing long-wave energy. The increased forcing drives further changes in Earth's energy balance and, over the longer term, in Earth's climate.[17]
Carbon cycle
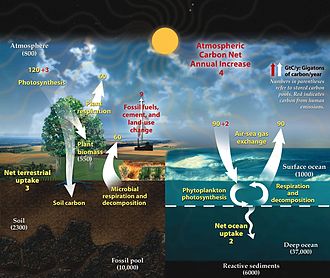
Atmospheric carbon dioxide plays an integral role in the Earth's carbon cycle whereby Template:CO2 is removed from the atmosphere by some natural processes such as photosynthesis and deposition of carbonates, to form limestones for example, and added back to the atmosphere by other natural processes such as respiration and the acid dissolution of carbonate deposits. There are two broad carbon cycles on Earth: the fast carbon cycle and the slow carbon cycle. The fast carbon cycle refers to movements of carbon between the environment and living things in the biosphere whereas the slow carbon cycle involves the movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, soil, rocks, and volcanism. Both cycles are intrinsically interconnected and atmospheric Template:CO2 facilitates the linkage.
Natural sources of atmospheric Template:CO2 include volcanic outgassing, the combustion of organic matter, wildfires and the respiration processes of living aerobic organisms. Man-made sources of Template:CO2 include the burning of fossil fuels, as well as some industrial processes such as cement making.

Natural sources of Template:CO2 are more or less balanced by natural carbon sinks, in the form of chemical and biological processes which remove Template:CO2 from the atmosphere. For example, the decay of organic material in forests, grasslands, and other land vegetation - including forest fires - results in the release of about 436 gigatonnes of Template:CO2 (containing 119 gigatonnes carbon) every year, while Template:CO2 uptake by new growth on land counteracts these releases, absorbing 451 Gt (123 Gt C).[54] Although much Template:CO2 in the early atmosphere of the young Earth was produced by volcanic activity, modern volcanic activity releases only 130 to 230 megatonnes of Template:CO2 each year.[55]
From the human pre-industrial era to 1940, the terrestrial biosphere represented a net source of atmospheric Template:CO2 (driven largely by land-use changes), but subsequently switched to a net sink with growing fossil carbon emissions.[56]
Carbon moves between the atmosphere, vegetation (dead and alive), the soil, the surface layer of the ocean, and the deep ocean. A detailed model has been developed by Fortunat Joos in Bern and colleagues, called the Bern model.[57] A simpler model based on it gives the fraction of Template:Co2 remaining in the atmosphere as a function of the number of years after it is emitted into the atmosphere:[58]
According to this model, 21.7% of the carbon dioxide released into the air stays there forever, but of course this is not true if carbon-containing material is removed from the cycle (and stored) in ways that are not operative at present (artificial sequestration).
Oceanic carbon cycle
The Earth's oceans contain a large amount of Template:CO2 in the form of bicarbonate and carbonate ions—much more than the amount in the atmosphere. The bicarbonate is produced in reactions between rock, water, and carbon dioxide.
From 1850 until 2022, the ocean has absorbed 26% of total anthropogenic emissions.[12] However, the rate at which the ocean will take it up in the future is less certain. Even if equilibrium is reached, including dissolution of carbonate minerals, the increased concentration of bicarbonate and decreased or unchanged concentration of carbonate ion will give rise to a higher concentration of un-ionized carbonic acid and dissolved Template:CO2. This higher concentration in the seas, along with higher temperatures, would mean a higher equilibrium concentration of Template:CO2 in the air.[59][60]
A study published in Science Advances in 2025 concluded that faster flow of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) at higher latitudes causes upwelling of isotopically light deep waters around Antarctica, likely increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and thereby potentially constituting a critical positive feedback for future warming.[61]
Effects of current increase
Direct effects
Direct effects of increasing CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere include increasing global temperatures, ocean acidification and a CO2 fertilization effect on plants and crops.[62]
Temperature rise on land
Temperature rise in oceans
Template:See also Template:Excerpt
Ocean acidification
CO2 fertilization effect
Other direct effects
Template:CO2 emissions have also led to the stratosphere contracting by 400 meters since 1980, which could affect satellite operations, GPS systems and radio communications.[63]
Indirect effects and impacts
Template:Excerpt Template:Excerpt
Approaches for reducing CO2 concentrations
File:Following Carbon Dioxide Through the Atmosphere.webm Template:Main Carbon dioxide has unique long-term effects on climate change that are nearly "irreversible" for a thousand years after emissions stop (zero further emissions). The greenhouse gases methane and nitrous oxide do not persist over time in the same way as carbon dioxide. Even if human carbon dioxide emissions were to completely cease, atmospheric temperatures are not expected to decrease significantly in the short term. This is because the air temperature is determined by a balance between heating, due to greenhouse gases, and cooling due to heat transfer to the ocean. If emissions were to stop, CO2 levels and the heating effect would slowly decrease, but simultaneously the cooling due to heat transfer would diminish (because sea temperatures would get closer to the air temperature), with the result that the air temperature would decrease only slowly. Sea temperatures would continue to rise, causing thermal expansion and some sea level rise.[59] Lowering global temperatures more rapidly would require carbon sequestration or geoengineering.
Various techniques have been proposed for removing excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Template:Excerpt
Concentrations in the geologic past


Estimates in 2023 found that the current carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere may be the highest it has been in the last 14 million years.[10] However the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report estimated similar levels 3 to 3.3 million years ago in the mid-Pliocene warm period. This period can be a proxy for likely climate outcomes with current levels of Template:CO2.[64]Template:Rp
Carbon dioxide is believed to have played an important effect in regulating Earth's temperature throughout its 4.54 billion year history. Early in the Earth's life, scientists have found evidence of liquid water indicating a warm world even though the Sun's output is believed to have only been 70% of what it is today. Higher carbon dioxide concentrations in the early Earth's atmosphere might help explain this faint young sun paradox. When Earth first formed, Earth's atmosphere may have contained more greenhouse gases and Template:CO2 concentrations may have been higher, with estimated partial pressure as large as Template:Convert, because there was no bacterial photosynthesis to reduce the gas to carbon compounds and oxygen. Methane, a very active greenhouse gas, may have been more prevalent as well.[65][66]
Carbon dioxide concentrations have shown several cycles of variation from about 180 parts per million during the deep glaciations of the Holocene and Pleistocene to 280 parts per million during the interglacial periods. Carbon dioxide concentrations have varied widely over the Earth's history. It is believed to have been present in Earth's first atmosphere, shortly after Earth's formation. The second atmosphere, consisting largely of nitrogen and Template:Chem was produced by outgassing from volcanism, supplemented by gases produced during the late heavy bombardment of Earth by huge asteroids.[67] A major part of carbon dioxide emissions were soon dissolved in water and incorporated in carbonate sediments.
The production of free oxygen by cyanobacterial photosynthesis eventually led to the oxygen catastrophe that ended Earth's second atmosphere and brought about the Earth's third atmosphere (the modern atmosphere) 2.4 billion years ago. Carbon dioxide concentrations dropped from 4,000 parts per million during the Cambrian period about 500 million years ago to as low as 180 parts per million 20,000 years ago .[2]
Drivers of ancient-Earth CO2 concentration
On long timescales, atmospheric Template:CO2 concentration is determined by the balance among geochemical processes including organic carbon burial in sediments, silicate rock weathering, and volcanic degassing. The net effect of slight imbalances in the carbon cycle over tens to hundreds of millions of years has been to reduce atmospheric Template:CO2. On a timescale of billions of years, such downward trend appears bound to continue indefinitely as occasional massive historical releases of buried carbon due to volcanism will become less frequent (as earth mantle cooling and progressive exhaustion of internal radioactive heat proceed further). The rates of these processes are extremely slow; hence they are of no relevance to the atmospheric Template:CO2 concentration over the next hundreds or thousands of years.
Photosynthesis in the geologic past
Over the course of Earth's geologic history Template:CO2 concentrations have played a role in biological evolution. The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide as sources of electrons, rather than water.[68] Cyanobacteria appeared later, and the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe,[69] which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. In recent geologic times, low Template:CO2 concentrations below 600 parts per million might have been the stimulus that favored the evolution of [[C4 carbon fixation|Template:C4]] plants which increased greatly in abundance between 7 and 5 million years ago over plants that use the less efficient [[C3 carbon fixation|Template:C3]] metabolic pathway.[70] At current atmospheric pressures photosynthesis shuts down when atmospheric Template:CO2 concentrations fall below 150 ppm and 200 ppm although some microbes can extract carbon from the air at much lower concentrations.[71][72]
Measuring ancient-Earth CO2 concentration


The most direct method for measuring atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations for periods before instrumental sampling is to measure bubbles of air (fluid or gas inclusions) trapped in the Antarctic or Greenland ice sheets. The most widely accepted of such studies come from a variety of Antarctic cores and indicate that atmospheric Template:CO2 concentrations were about 260–280 ppm immediately before industrial emissions began and did not vary much from this level during the preceding 10,000 years.[73][74] The longest ice core record comes from East Antarctica, where ice has been sampled to an age of 800,000 years.[75] During this time, the atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration has varied between 180 and 210 ppm during ice ages, increasing to 280–300 ppm during warmer interglacials.[76][77]
Template:CO2 mole fractions in the atmosphere have gone up by around 35 percent since the 1900s, rising from 280 parts per million by volume to 387 parts per million in 2009. One study using evidence from stomata of fossilized leaves suggests greater variability, with Template:CO2 mole fractions above 300 ppm during the period ten to seven thousand years ago,[78] though others have argued that these findings more likely reflect calibration or contamination problems rather than actual CO2 variability.[79][80] Because of the way air is trapped in ice (pores in the ice close off slowly to form bubbles deep within the firn) and the time period represented in each ice sample analyzed, these figures represent averages of atmospheric concentrations of up to a few centuries rather than annual or decadal levels.
Ice cores provide evidence for greenhouse gas concentration variations over the past 800,000 years. Both CO2 and Template:Chem concentrations vary between glacial and interglacial phases, and these variations correlate strongly with temperature. Direct data does not exist for periods earlier than those represented in the ice core record, a record that indicates that CO2 mole fractions stayed within a range of 180 ppm to 280 ppm throughout the last 800,000 years, until the increase of the last 250 years. However, various proxy measurements and models suggest larger variations in past epochs: 500 million years ago CO2 levels were likely 10 times higher than now.[81]
Various proxy measurements have been used to try to determine atmospheric CO2 concentrations millions of years in the past. These include boron and carbon isotope ratios in certain types of marine sediments, and the numbers of stomata observed on fossil plant leaves.[70]
Phytane is a type of diterpenoid alkane. It is a breakdown product of chlorophyll, and is now used to estimate ancient Template:CO2 levels.[82] Phytane gives both a continuous record of Template:CO2 concentrations but it also can overlap a break in the Template:CO2 record of over 500 million years.[82]
600 to 400 million years ago
There is evidence for high Template:CO2 concentrations of over 6,000 ppm between 600 and 400 million years ago, and of over 3,000 ppm between 200 and 150 million years ago.[83]Template:Failed verification
Indeed, higher CO2 concentrations are thought to have prevailed throughout most of the Phanerozoic Eon, with concentrations four to six times current concentrations during the Mesozoic era, and ten to fifteen times current concentrations during the early Palaeozoic era until the middle of the Devonian period, about 400 million years ago.[84][85][86] The spread of land plants is thought to have reduced CO2 concentrations during the late Devonian, and plant activities as both sources and sinks of CO2 have since been important in providing stabilizing feedbacks.[87]
Earlier still, a 200-million year period of intermittent, widespread glaciation extending close to the equator (Snowball Earth) appears to have been ended suddenly, about 550 Ma, by a colossal volcanic outgassing that raised the Template:CO2 concentration of the atmosphere abruptly to 12%, about 350 times modern levels, causing extreme greenhouse conditions and carbonate deposition as limestone at the rate of about 1 mm per day.[88] This episode marked the close of the Precambrian Eon, and was succeeded by the generally warmer conditions of the Phanerozoic, during which multicellular animal and plant life evolved. No volcanic CO2 emission of comparable scale has occurred since. In the modern era, emissions to the atmosphere from volcanoes are approximately 0.645 billion tons of Template:CO2 per year, whereas humans contribute 29 billion tons of Template:CO2 each year.[89][88][90][91]
60 to 5 million years ago
Atmospheric Template:CO2 concentration continued to fall after about 60 million years ago. About 34 million years ago, the time of the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event and when the Antarctic ice sheet started to take its current form, Template:CO2 was about 760 ppm,[92] and there is geochemical evidence that concentrations were less than 300 ppm by about 20 million years ago. Decreasing Template:CO2 concentration, with a tipping point of 600 ppm, was the primary agent forcing Antarctic glaciation.[93] Low Template:CO2 concentrations may have been the stimulus that favored the evolution of [[C4 carbon fixation|Template:C4]] plants, which increased greatly in abundance between 7 and 5 million years ago.[70]
See also
References
External links
- Current global map of carbon dioxide concentrations.
- Global Carbon Dioxide Circulation (NASA; 13 December 2016)
- Video (03:10) – A Year in the Life of Earth's Template:CO2 (NASA; 17 November 2014)
Template:Portal barTemplate:Climate changeTemplate:Authority control
fr:Dioxyde de carbone#CO2 dans l'atmosphère terrestre
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Template:Cite book
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Template:Cite web
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ IPCC (2022) Summary for policy makers Template:Webarchive in Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Template:Webarchive, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Template:Cite journal Template:Creative Commons text attribution notice
- ↑ "Parts per million" refers to the number of carbon dioxide molecules per million molecules of dry air. Template:Cite web Updated monthly.
- ↑ Template:Cite web Latest figure, and graphs of trend; frequently updated
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web Alt URL Template:Webarchive
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Eyring, V., N.P. Gillett, K.M. Achuta Rao, R. Barimalala, M. Barreiro Parrillo, N. Bellouin, C. Cassou, P.J. Durack, Y. Kosaka, S. McGregor, S. Min, O. Morgenstern, and Y. Sun, 2021: Chapter 3: Human Influence on the Climate System Template:Webarchive. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Template:Webarchive [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 423–552, Template:Doi
- ↑ Template:Cite
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite news
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite news
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ WDCGG webpage Template:Webarchive Retrieved 2 March 2016
- ↑ RAMCES webpage
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ e.g. Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 Friedlingstein, P., Jones, M., O'Sullivan, M., Andrew, R., Hauck, J., Peters, G., Peters, W., Pongratz, J., Sitch, S., Le Quéré, C. and 66 others (2019) "Global carbon budget 2019". Earth System Science Data, 11(4): 1783–1838. Template:Doi.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Calculated from file global.1751_2013.csv in [1] Template:Webarchive from the Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center.
- ↑ IEA (2023), The world’s top 1% of emitters produce over 1000 times more Template:CO2 than the bottom 1%, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/commentaries/the-world-s-top-1-of-emitters-produce-over-1000-times-more-co2-than-the-bottom-1 , License: CC BY 4.0
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ A concise description of the greenhouse effect is given in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report, "What is the Greenhouse Effect?" FAQ 1.3 – AR4 WGI Chapter 1: Historical Overview of Climate Change Science Template:Webarchive, IPCC Fourth Assessment Report, Chapter 1, p. 115: "To balance the absorbed incoming [solar] energy, the Earth must, on average, radiate the same amount of energy back to space. Because the Earth is much colder than the Sun, it radiates at much longer wavelengths, primarily in the infrared part of the spectrum (see Figure 1). Much of this thermal radiation emitted by the land and ocean is absorbed by the atmosphere, including clouds, and reradiated back to Earth. This is called the greenhouse effect."
Stephen H. Schneider, in Geosphere-biosphere Interactions and Climate, Lennart O. Bengtsson and Claus U. Hammer, eds., Cambridge University Press, 2001, Template:ISBN, pp. 90–91.
E. Claussen, V.A. Cochran, and D.P. Davis, Climate Change: Science, Strategies, & Solutions, University of Michigan, 2001. p. 373.
A. Allaby and M. Allaby, A Dictionary of Earth Sciences, Oxford University Press, 1999, Template:ISBN, p. 244. - ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal, supplement to Climate impacts of energy technologies depend on emissions timing
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Gulev, S.K., P.W. Thorne, J. Ahn, F.J. Dentener, C.M. Domingues, S. Gerland, D. Gong, D.S. Kaufman, H.C. Nnamchi, J. Quaas, J.A. Rivera, S. Sathyendranath, S.L. Smith, B. Trewin, K. von Schuckmann, and R.S. Vose, 2021: Chapter 2: Changing State of the Climate System. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 287–422, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.004.
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 70.2 Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite news
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Vostok Ice Core Data Template:Webarchive, ncdc.noaa.gov Template:Webarchive
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ File:Phanerozoic Carbon Dioxide.png
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite news
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ See also: Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite journal