Harmonic spectrum
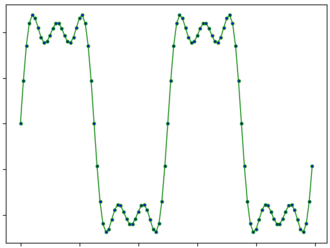
A harmonic spectrum is a spectrum containing only frequency components whose frequencies are whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency; such frequencies are known as harmonics. "The individual partials are not heard separately but are blended together by the ear into a single tone."[1]
In other words, if is the fundamental frequency, then a harmonic spectrum has the form
A standard result of Fourier analysis is that a function has a harmonic spectrum if and only if it is periodic.
See also
References
Template:Acoustics Template:Mathanalysis-stub Template:Signal-processing-stub
- ↑ Benward, Bruce and Saker, Marilyn (1997/2003). Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I, p.xiii. Seventh edition. McGraw-Hill. Template:ISBN.