Mains electricity by country
Template:Short description Template:Broader Template:Use dmy dates
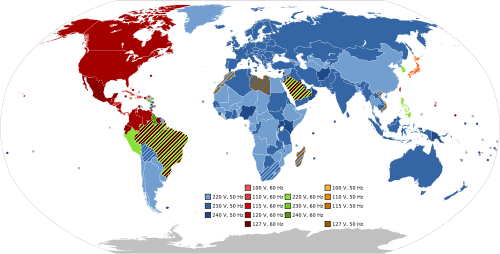
Mains electricity by country includes a list of countries and territories, with the plugs, voltages and frequencies they commonly use for providing electrical power to low voltage appliances, equipment, and lighting typically found in homes and offices. (For industrial machinery, see industrial and multiphase power plugs and sockets.) Some countries have more than one voltage available. For example, in North America, a unique split-phase system is used to supply to most premises that works by center tapping a 240 volt transformer. This system is able to concurrently provide 240 volts and 120 volts. Consequently, this allows homeowners to wire up both 240 V and 120 V circuits as they wish (as regulated by local building codes). Most sockets are connected to 120 V for the use of small appliances and electronic devices, while larger appliances such as dryers, electric ovens, ranges and EV chargers use dedicated 240 V sockets. Different sockets are mandated for different voltage or maximum current levels.
Voltage, frequency, and plug type vary, but large regions may use common standards. Physical compatibility of receptacles may not ensure compatibility of voltage, frequency, or connection to earth (ground), including plugs and cords. In some areas, older standards may still exist. Foreign enclaves, extraterritorial government installations, or buildings frequented by tourists may support plugs not otherwise used in a country, for the convenience of travellers.
Main reference sourceTemplate:SndIEC World Plugs
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) publishes a web microsite World Plugs[1] which provides the main source for this page, except where other sources are indicated. World Plugs includes some history, a description of plug types, and a list of countries giving the type(s) used and the mains voltage and frequency.
Although useful for quick reference, especially for travellers, IEC World Plugs may not be regarded as totally accurate, as illustrated by the examples in the plugs section below, and errors may exist.
Voltages
Voltages in this article are the nominal single-phase supply voltages, or split-phase supply voltages. Three-phase and industrial loads may have other voltages.
All voltages are root mean square (RMS) voltage; the peak AC voltage is greater by a factor of , and the peak-to-peak voltage greater by a factor of Template:Clear
Plugs

Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline • Template:Legend-inline
The system of plug types using a single letter (from A to O) used here is from World Plugs, which defines the plug type letters in terms of a general description, without making reference to specific standards. Where a plug does not have a specific letter code assigned to it, then it may be defined by the style sheet number listed in IEC TR 60083.[2] Template:-
Identification guide
-
Type A (NEMA 1–15, US 2 pin); max 15 A at 125 V, ungrounded
-
Type B (NEMA 5–15, US 3 pin); max 15 A at 125 V
-
CEE 7/17 2-pin plug; max 16 A, ungrounded
-
Type D (BS 546 5 A)
-
Type E (French) – CEE 7/6 plug & CEE 7/5 socket; max 16 A
-
Type F ("Schuko") – CEE 7/4 plug & CEE 7/3 socket; max 16 A
-
CEE 7/7 plug (combines earthing methods of Types E and F); max 16 A
-
Type H (SI 32 Israel)
-
Type I (AS/NZS 3112, GB/T 1002, IRAM 2073 and 2071); Argentinian version has reversed polarity compared to Chinese and Australasian versions; max 10–20 A
-
Type J (SN 441011, Switzerland); max 10 A
-
Type K (SRAF 1962/DB Denmark)
-
Type L (CEI 23-50)
-
Type M (15 A BS 546)
-
Type N (NBR 14136, Brazil and SANS 164-2, South Africa); max 10–20 A
Table of mains voltages, frequencies, and plugs
| Country or territory | Plug typeTemplate:Efn | National plug standard[2] |
Voltage | Frequency[7] | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential[7] | Three-phase[8] | |||||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, I | NEMA 1-15 NEMA 5-15 AS/NZS 3112 |
120 V | 208 V | 60 Hz | Type I is used due to close proximity with independent western neighbor Samoa. |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 110 V | 120/208 V 127/220 V 240/415 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 230 V | 400 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, I | IRAM 2073 | 220 V[9] | 380 V | 50 Hz | Line and neutral reversed compared to Chinese and Australian/NZ type I. |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, F | 127 V | 220 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Except: Western Australia, Fiji, Tonga and Papua New Guinea: 240/415 V Solomon Islands: 220/380 |
| Template:Flag | C F |
ÖVE-IG/EN 50075 ÖVE/ÖNORM E 8620 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, C, D, G[10] | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 115 V | 200 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V[11] | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | Template:Nowrap | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | A, B, G | 110 V 220 V |
190 V 380 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, F, G, M | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C | 115 V 230 V |
400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag,[12][13][14][15] Template:Flag and Template:Flag |
A, B | 127 V | 220 V | 50 Hz | Sockets for 220-240 V European type C plugs are typically available at hotels; some buildings modify voltage, so travellers are advised to check before plugging in. Type F are also available at some hotels. | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, G, M | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, N | NBR 14136 | 127 V 220 V[16] |
220 V 380 V |
60 Hz[17] | Before standardization, socket types varied: C (very old installations), I (for air conditioners), and combinations like A/C and A/B/C. |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 110 V | 190 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, C, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Sockets for British type G plugs are mainly found at some hotels and never in households. | |
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B NEMA 14-30, NEMA 14-50 |
CSA C22.2 No. 42[18] | 120 V[19] 240 V |
120/208 V 240 V 277/480 V 347/600 V |
60 Hz | NEMA 5-20R outlets, which are similar to type B but have a T-shaped neutral slot, are sometimes used for higher current 120 V equipment (up to 20 A). Homes are typically provided with 120/240 V split-phase power; NEMA 14-30R and 14-50R receptacles are provided on 240 V circuits for clothes dryers and electric stoves.[20] |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 240 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, E, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F, L | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | Type L is the national official standard; C and F are compatible. Schuko or type F plugs are often used for high power appliances. | |
| Template:Flag | A, C, I | GB/T 1002 GB/T 2099 |
220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | Type C was removed from GB/T 1002-2021, but A/C hybrid sockets still appear in old installations. LineTemplate:Fix/neutral reversed compared to Argentinian type I. |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V[21] | 120/208 V 277/480 V 120/240 V 240/208/120 V 240 V 480 V |
60 Hz[22] | NEMA 5-20R outlets, which are similar to type B but have a T-shaped neutral slot, are sometimes used for higher current 120 V commercial equipments (up to 20 A). On the other hand, NEMA 10-50P outlets are sometimes used for 208 V and 240 V industrial equipments (up to 50 A). | |
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag [23] |
C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V 240 V 480 V[24] |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, L | 110 V | 190 V 220 V |
60 Hz | Some modern hotels have 220 V sockets for European 2-pin plugs (Type C).[25] | |
| Template:Flag | A,[26] B, F[27] | 127 V[26][28] | 220 V 380 V |
50 Hz[26] | Some hotels and apartments have 220 V European sockets.[29] | |
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | ČSN 35 4516 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C E, F, K |
DS/EN 50075 DS 60884-2-D1[30] |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type E and F sockets are rare but legal, type E, F and 7/7 plugs work as type C (unearthed). |
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C | 110 V | 120/208 V 277/480 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V 480 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 115 V | 208 V 220 V 440 V 480 V[31] |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, L | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | M | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, F, L | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | Type E is very rare because Ethiopia never had French influences. | |
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, F, K | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Same as in Denmark. | |
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | Same as in Australia. |
| Template:Flag | C F |
SFS-EN 50075 SFS 5610 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C E |
NF EN 50075 NF C 61-314 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, E, F | 110 V 220 V |
380 V | 60 Hz[32] 50 Hz |
||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C F IEC 60309 |
DIN VDE 0620 DIN 49441 DIN EN 60309 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, F, K | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, E | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 110 V | 190 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F, K | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, D, G | 110 V 220 V[33] |
190 V | 60 Hz 50 Hz[33] |
Conversion of 50 Hz distribution to 60 Hz is ongoing.[34] | |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 110 V | 220/380 V 110/220 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 110 V | 208 V 230 V 240 V 460 V 480 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G D, M[35] |
BS 1363 BS 546 |
220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | Type G is most common. |
| Template:Flag | C F |
MSZ EN 50075 MSZ 9781-2 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, M | IS 1293:2019[36] | 230 V[7] | 400 V[37] | 50 Hz | The combination of a type C, E or F plug with a type D socket may often be workable, but it is unsafe to use.[38] From August 2015, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) began clamping down on the sale of imported products with type C/E/F plugs by pushing manufacturers and importers to comply with the IS 1293 standard.[39] In June 2022, BIS began enforcing the standard through mandatory certification of both imported and domestic products.[40] |
| Template:Flag | C, F | SNI 04-3892.1.1-2003 | 230 V[41] | 400 V[41] | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | I.S. 401[42] | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type G is the only general purpose outlet type in use in Ireland. Bathrooms may have shaver sockets. These accept 2.5 amp Europlug CEE 7/16 and UK type BS 4573 plugs, which used on shavers and toothbrushes. They do not accept larger type C plugs and general purpose outlets are generally banned in bathrooms / wet areas. Some hotels may also provide a type F (Schuko) socket as a convenience for European visitors. |
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | Self-governing British crown dependency, but generally uses UK technical standards. | |
| Template:Flag | C, H | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C F, L |
CEI 23-34 CEI 23-50 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type L uses two gauges of plug and socket. The 10 amp version has pin spacing that is compatible with Europlug. The 16 amp version uses wider pin spacing and larger pins. Hybrid outlets that accept both types are common and some also accept type F. NB: 16 amp type C plugs, such as CEE 7/17 commonly found on hairdryers, will not fit type L outlets and need an adapter, or should be used with a type F or hybrid type L/F outlet. |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 110 V | 190 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | JIS C 8303 | 100 V 200 V |
200 V 415 V |
50 Hz 60 Hz |
East Japan 50 Hz (Tokyo, Kawasaki, Sapporo, Yokohama, and Sendai); West Japan 60 Hz (Okinawa, Osaka, Kyoto, Kobe, Nagoya, Hiroshima). 120 V in military facilities in Okinawa.[43] Majority of sockets accept only type A plugs. See Energy in Japan for more. |
| Template:Flag | G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | B, C, D, F, G, J | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | 230/400 V voltage is defined in "GOST 29322-2014 Mezhgosudarstvennyi Standart Napryazheniya Standartnye". | |
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F[44] | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, E, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Some buildings and households have hybrid sockets compatible with type A, B and C. | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, D, G | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type C sockets are the most frequent. Many buildings and households have double-use sockets compatible with type A and C. | |
| Template:Flag | M | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, E, F | 120 V 220 V |
208 V | 60 Hz 50 Hz |
||
| Template:Flag | C, D, F, L | 127 V 230 V |
400 V | 50 Hz | Barca, Benghazi, Derna, Sabha & Tobruk 230 V.Template:Citation needed | |
| Template:Flag | C, J | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, F, G, M | 230 V[45] | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, E, J, K | 127 V 220 V |
380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C[46] G[46] M[46][47] |
MS 1578:2003[46] MS 589:PT.1:1997[46] MS 1577:2003[46] |
230 V[48] | 400 V | 50 Hz | TypeTemplate:NbspG is most common. Devices using an Europlug (Type C) may be sold but require an adaptor, since there are usually no sockets for them. Type M is used mainly for air conditioners and boilers. Bathrooms may have shaver supply units.[49] |
| Template:Flag | D, G, J, K, L | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, F | 220 V | 220 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | NMX-J-163-ANCE | 120 V 127 V |
240 V 220 V |
60 Hz | Both 120/240 V split-phase and 127/220 V three-phase are used. |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, E, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, F | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 230 V | 400 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 127 V 220 V |
380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F, M | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, C, D, F, G, I | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, M | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, D, M | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C F |
EN 50075 NEN 1020 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | Despite that New Caledonia is a French territory, German Schuko type F sockets are used instead of French type E sockets. | |
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Line and neutral reversed compared to Argentinian type I. |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, D, E, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | A, C, F | 110 V 220 V |
380 V | 60 Hz 50 Hz |
||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C F |
NEK EN 50075 NEK 502 |
230 V | 230 V 400 V |
50 Hz | 230 V on IT grid, and 400 V on TN grid. |
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, G, M | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 208 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, H | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B | 110 V | 240 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, N | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C F, L[50] |
220 V | 380 V 440 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C | 230 V[7][51] | 400 V | 60 Hz | Many buildings and households have double-use sockets compatible with type A and C, and often also with B for grounded plugs. NEMA 6-15 is used for air conditioners. | |
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, E | BN-88/3064 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, E, F | NP 1260 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type E is very rare, used only in very old installations. |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V | 480 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, F, G, L | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V[11] | 400 V | 50 Hz | USSR (along with much of Eastern Europe) used GOST sockets with 4.0 mm pins similar to type C plugs and the 4.8 mm standard used by type E & F.[52] | |
| Template:Flag | C, E, F, G[53] | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Types C & E are official; type G has become common as well because of imports from Uganda, Tanzania and Kenya; type F is very rare.[54] | |
| Template:Flag | G[55] | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag (French) | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag (Dutch) | A, B | 120 V 127 V |
220 V | 60 Hz | 127/220 V AC 60 Hz three-phase service. | |
| Template:Flag | A, B, D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, G | 240 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E, F[56] | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, E, G, I, K | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F, L | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G | SASO 2203 | 220 V
230 V |
400 V | 50 Hz 60 Hz |
|
| Template:Flag | C, D, E, K | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C F |
JUS N.E3.552 JUS N.E3.553 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 240 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C G M |
- SS 145 SS 472 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type C requires adaptor. Hotel bathrooms may have shaver supply units (but usually not in homes). Type M is used mainly for air conditioners, ovens, clothes dryers and some high-powered industrial/office equipment. |
| Template:Flag | C, E, F | STN 34 4516 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G, I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, G | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, M, N | SANS 164 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | KS C 8305 | 220 V | 380 V | 60 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F | UNE 20315 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type E is extremely rare, but it may appear in some buildings, such as the University Carlos III of Madrid. Almost every Spanish plug would work on Type E sockets. |
| Template:Flag | D, G, M | SLS 734 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Only type G permitted to be manufactured or imported from August 2017.[57] |
| Template:Flag | C, D, F, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, F | 127 V | 220 V 400 V |
60 Hz | Type A and B tend to be very common because standard sockets can't accommodate such voltage. | |
| Template:Flag | C F IEC 60309 |
SS-EN 50075 SS 428 08 34 SS-EN 60309 |
230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Bathrooms may have shaver supply units. |
| Template:Flag | C, J | SN SEV 1011:2009[58][59] | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, E, L | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A B |
CNS 690 CNS 15767 |
110 V | 220 V 380 V |
60 Hz | Sockets in older buildings are often unearthed and accept only type A plugs. |
| Template:Flag | C, F, I | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, O | TIS 166-2549[60][61] (defines grounded and ungrounded variants of the national plug type O and a socket specifically for it; also standardizes the combisockets that so far are exclusively used in Thailand) | 220 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Sockets are combisockets that accept American (A, B) and Europlugs (C) as well as the newly introduced Thai plug (O). Sockets also accept French and Schuko plugs (E, F), but unsafely (without establishing earth contact), therefore the sale of appliances with E or F plugs has been banned. |
| Template:Flag (East Timor) | C, E, F, I | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 115 V | 115/230 V 230/400 V |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, E | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V[62] | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | B, C, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | G | 240 V | 415 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, F | 230 V[63][64] | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | G[65] | BS 1363[65] | 230 V[66] | 400 V[66] | 50 Hz[66] | Bathrooms may have shaver supply units.[65] |
| Template:Flag | G[67] D, M[68] |
BS 1363 BS 546 |
230 V[69] | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type D mostly historical, nowadays used only for remotely switched lighting and similar. Type M historically used in domestic installations, now only for stage lighting (where they are increasingly replaced with Ceeform). Bathrooms may have shaver supply units. |
| Template:Anchor Template:Flag | A, B NEMA 14-30, NEMA 14-50 |
NEMA 1-15, NEMA 5-15 NEMA 14-30, NEMA 14-50 |
120 V 240 V |
120/208 V 277/480 V 120/240 V 240 V 480 V |
60 Hz | NEMA 5-20R outlets, which are similar to type B but have a T-shaped neutral slot, are sometimes used for higher current 120 V equipment (up to 20 A). |
| Template:Flag | A B |
NEMA 1-15P NEMA 5-15P |
110 V | 190 V | 60 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | C, F, I, L | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | Type I was the main standard until the 1990s, and still appears in old installations. | |
| Template:Flag | C, E, F | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, G, I | AS/NZS 3112 | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | |
| Template:Flag | A, B | 120 V 208 V 240 V |
115/220 V 220/440 V 230/460 V[70] |
60 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | A, B, C, F | TCVN 6188-1 | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | Most households use unearthed hybrid sockets that accept type A and C plugs. Hybrid sockets that accept type A, B and C plugs are sometimes used in commercial installations. Type E or F (French/Schuko) plugs are frequently plugged into hybrid sockets, though this is somewhat unsafe, as no earth contact is made. |
| Template:Flag | A, D, G | 240 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | C, D, G | 230 V | 400 V | 50 Hz | ||
| Template:Flag | D, G | 220 V | 380 V | 50 Hz | ||
Notes
See also
- Delta-wye transformer
- Electrical wiring
- Electric power transmission
- Electrification
- Electrical grid
- List of railway electrification systems
- Mains electricity
References
External links
fi:Verkkovirta ur:مینز برق بلحاظ ملک
- ↑ World Plugs Template:Webarchive. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Retrieved on 2018-06-05.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 IEC/TR 60083 ed7.0: Plugs and socket-outlets for domestic and similar general use standardized in member countries of IEC. International Electrotechnical Commission, October 2015. This 421-page technical report describes many national standards for domestic plugs and sockets. The first edition was published in January 1957. The 7th edition was approved in December 2012 and was published on 29 October 2015.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Reglamentado por AEA 90364, IRAM 2001 & IEC 60083
- ↑ Bangladesh Gazette | February 11, 2021 by Ministry of Housing and Public Works, Page: 1967. Archived from original on 2022-08-12.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Template:Cite web Document gost-29322-92 via Google Translate: "The nominal voltages of the existing 220/380 and 240/415 V networks should be gradually changed to the recommended value of 230/400 V. Until 2003, as a first stage, power supply companies in countries with a 220/380 V network should lead the voltage to The value of 230/400 V (GOST 29322-92 (IEC 38-83) Standard voltage%). Electricity supply companies in regions with 240/415 V network should also bring this voltage to the value 230/400 V (GOST 29322-92 (IEC 38-83) Standard voltage%). After 2003, the range of 230/400 V ± 10% should be reached. Then, the issue of reducing the limits will be considered."
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Template:Cite web
- ↑ https://www.power-plugs-sockets.com/gb/curacao/
- ↑ Confirmed 127 V by looking at Aqualetric residential electricity meter
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 History of Guyana Power and Light Template:Webarchive. Gplinc.com. Retrieved on 2014-01-01.
- ↑ GPL Converting Parts of the City to 60 Hz, retrieved 2009 July 31 Template:Webarchive. Stabroeknews.com (2009-07-10). Retrieved on 2014-01-01.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite news
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ I.S. 401, "Safety requirements for rewirable and non-rewirable 13 A fused plugs for normal and rough use having insulating sleeves on line and neutral pins", NSAI (National Standards Authority of Ireland), (1997), Dublin
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ https://www.power-plugs-sockets.com/gb/kosovo/
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 46.3 46.4 46.5 Plug Top/Plug (15 A and below) -Energy Commission of Malaysia. Archived from the original 2015-01-07.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Voltan Nominal Template:Webarchive. Malaysian Energy Commission Notice (Nominal Voltage - 2008-01-01). Retrieved on 2019-02-11
- ↑ Template:Cite web (MS 1579:2003 is adaptor for Europlugs.)
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ ГОСТ 7396.1–89 - Plugs (Electrical) and socket-outlets for domestic and similar general use. Standards. Template:Webarchive Elec.ru (2013-01-30). Retrieved on 2013-02-05.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ https://www.power-plugs-sockets.com/gb/saint-helena-ascension-and-tristan-da-cunha/
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite press release
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ TIS 166-2549 (2006): Thai Industrial Standards for Plugs and socket-outlets for household and similar purposes: plugs and socket-outlets with rated voltage not exceeding 250 V (English translation) Archived from the original 2016-07-07.
- ↑ TIS 166-2549 (2006): Thai Industrial Standard for Plugs and socket-outlets for household and similar purposes: plugs and socket-outlets with rated voltage not exceeding 250 V (Original Thai) Template:ISBN
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Temporarily the nominal voltage in the low-voltage network is 220 V
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 65.2 Template:Cite book
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 66.2 Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Cite web
















![Type O (Thai TIS 166-2549 mains plug);[3] max 16 A](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/51/Thai_TIS_166-2549_mains_plug.jpg/250px-Thai_TIS_166-2549_mains_plug.jpg)
![So-called "universal socket" which meets no standard[4] but accepts a number of different plug types (criticized as non-compliant and unsafe)[5][6]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8b/Multi_plug.jpg/120px-Multi_plug.jpg)