Image (category theory)
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, the image of a morphism is a generalization of the image of a function.
General definition
Given a category and a morphism in , the image[1] of is a monomorphism satisfying the following universal property:
- There exists a morphism such that .
- For any object with a morphism and a monomorphism such that , there exists a unique morphism such that .
Remarks:
- such a factorization does not necessarily exist.
- is unique by definition of monic.
- , therefore by monic.
- is monic.
- already implies that is unique.

The image of is often denoted by or .
Proposition: If has all equalizers then the in the factorization of (1) is an epimorphism.[2]
Second definition
In a category with all finite limits and colimits, the image is defined as the equalizer of the so-called cokernel pair , which is the cocartesian of a morphism with itself over its domain, which will result in a pair of morphisms , on which the equalizer is taken, i.e. the first of the following diagrams is cocartesian, and the second equalizing.[3]
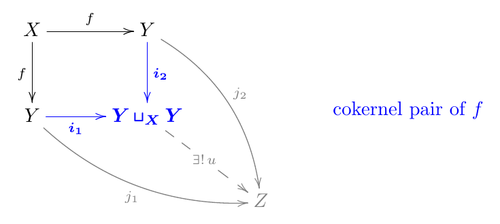

Remarks:
- Finite bicompleteness of the category ensures that pushouts and equalizers exist.
- can be called regular image as is a regular monomorphism, i.e. the equalizer of a pair of morphisms. (Recall also that an equalizer is automatically a monomorphism).
- In an abelian category, the cokernel pair property can be written and the equalizer condition . Moreover, all monomorphisms are regular.
Examples
In the category of sets the image of a morphism is the inclusion from the ordinary image to . In many concrete categories such as groups, abelian groups and (left- or right) modules, the image of a morphism is the image of the correspondent morphism in the category of sets.
In any normal category with a zero object and kernels and cokernels for every morphism, the image of a morphism can be expressed as follows:
- im f = ker coker f
In an abelian category (which is in particular binormal), if f is a monomorphism then f = ker coker f, and so f = im f.
Essential Image
A related notion to image is essential image.[4]
A subcategory of a (strict) category is said to be replete if for every , and for every isomorphism , both and belong to C.
Given a functor between categories, the smallest replete subcategory of the target n-category B containing the image of A under F.
See also
References
- ↑ Template:Citation Section I.10 p.12
- ↑ Template:Citation Proposition 10.1 p.12
- ↑ Template:Citation Definition 5.1.1
- ↑ Template:Cite web