Matroid polytope
Template:Short description In mathematics, a matroid polytope, also called a matroid basis polytope (or basis matroid polytope) to distinguish it from other polytopes derived from a matroid, is a polytope constructed via the bases of a matroid. Given a matroid , the matroid polytope is the convex hull of the indicator vectors of the bases of .
Definition
Let be a matroid on elements. Given a basis of , the indicator vector of is
where is the standard th unit vector in . The matroid polytope is the convex hull of the set
Examples
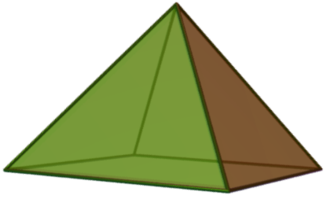

- Let be the rank 2 matroid on 4 elements with bases
- That is, all 2-element subsets of except . The corresponding indicator vectors of are
- The matroid polytope of is
- These points form four equilateral triangles at point , therefore its convex hull is the square pyramid by definition.
- Let be the rank 2 matroid on 4 elements with bases that are all 2-element subsets of . The corresponding matroid polytope is the octahedron. Observe that the polytope from the previous example is contained in .
- If is the uniform matroid of rank on elements, then the matroid polytope is the hypersimplex .[1]
Properties
- A matroid polytope is contained in the hypersimplex , where is the rank of the associated matroid and is the size of the ground set of the associated matroid.[2] Moreover, the vertices of are a subset of the vertices of .
- Every edge of a matroid polytope is a parallel translate of for some , the ground set of the associated matroid. In other words, the edges of correspond exactly to the pairs of bases that satisfy the basis exchange property: for some [2] Because of this property, every edge length is the square root of two. More generally, the families of sets for which the convex hull of indicator vectors has edge lengths one or the square root of two are exactly the delta-matroids.
- Matroid polytopes are members of the family of generalized permutohedra.[3]
- Let be the rank function of a matroid . The matroid polytope can be written uniquely as a signed Minkowski sum of simplices:[3]
- where is the ground set of the matroid and is the signed beta invariant of :
Related polytopes
Independence matroid polytope
The matroid independence polytope or independence matroid polytope is the convex hull of the set
The (basis) matroid polytope is a face of the independence matroid polytope. Given the rank of a matroid , the independence matroid polytope is equal to the polymatroid determined by .
Flag matroid polytope
The flag matroid polytope is another polytope constructed from the bases of matroids. A flag is a strictly increasing sequence
of finite sets.[4] Let be the cardinality of the set . Two matroids and are said to be concordant if their rank functions satisfy
Given pairwise concordant matroids on the ground set with ranks , consider the collection of flags where is a basis of the matroid and . Such a collection of flags is a flag matroid . The matroids are called the constituents of . For each flag in a flag matroid , let be the sum of the indicator vectors of each basis in
Given a flag matroid , the flag matroid polytope is the convex hull of the set
A flag matroid polytope can be written as a Minkowski sum of the (basis) matroid polytopes of the constituent matroids:[4]
References
- ↑ Template:Citation. See in particular the remarks following Prop. 8.20 on p. 114.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Template:Cite journal
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Template:Cite journal
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Template:Cite journal