Lindley's paradox
Template:Short description Lindley's paradox is a counterintuitive situation in statistics in which the Bayesian and frequentist approaches to a hypothesis testing problem give different results for certain choices of the prior distribution. The problem of the disagreement between the two approaches was discussed in Harold Jeffreys' 1939 textbook;[1] it became known as Lindley's paradox after Dennis Lindley called the disagreement a paradox in a 1957 paper.[2]
Although referred to as a paradox, the differing results from the Bayesian and frequentist approaches can be explained as using them to answer fundamentally different questions, rather than actual disagreement between the two methods.
Nevertheless, for a large class of priors the differences between the frequentist and Bayesian approach are caused by keeping the significance level fixed: as even Lindley recognized, "the theory does not justify the practice of keeping the significance level fixed" and even "some computations by Prof. Pearson in the discussion to that paper emphasized how the significance level would have to change with the sample size, if the losses and prior probabilities were kept fixed".[2] In fact, if the critical value increases with the sample size suitably fast, then the disagreement between the frequentist and Bayesian approaches becomes negligible as the sample size increases.[3]
The paradox continues to be a source of active discussion.[3][4][5][6][7]
Description of the paradox
The result of some experiment has two possible explanationsTemplate:Snd hypotheses and Template:Snd and some prior distribution representing uncertainty as to which hypothesis is more accurate before taking into account .
Lindley's paradox occurs when
- The result is "significant" by a frequentist test of indicating sufficient evidence to reject say, at the 5% level, and
- The posterior probability of given is high, indicating strong evidence that is in better agreement with than
These results can occur at the same time when is very specific, more diffuse, and the prior distribution does not strongly favor one or the other, as seen below.
Numerical example
The following numerical example illustrates Lindley's paradox. In a certain city 49,581 boys and 48,870 girls have been born over a certain time period. The observed proportion of male births is thus Template:Val/Template:Val ≈ 0.5036. We assume the fraction of male births is a binomial variable with parameter We are interested in testing whether is 0.5 or some other value. That is, our null hypothesis is and the alternative is
Frequentist approach
The frequentist approach to testing is to compute a p-value, the probability of observing a fraction of boys at least as large as assuming is true. Because the number of births is very large, we can use a normal approximation for the fraction of male births with and to compute
We would have been equally surprised if we had seen Template:Val female births, i.e. so a frequentist would usually perform a two-sided test, for which the p-value would be In both cases, the p-value is lower than the significance level α = 5%, so the frequentist approach rejects as it disagrees with the observed data.
Bayesian approach
Assuming no reason to favor one hypothesis over the other, the Bayesian approach would be to assign prior probabilities and a uniform distribution to under and then to compute the posterior probability of using Bayes' theorem:
After observing boys out of births, we can compute the posterior probability of each hypothesis using the probability mass function for a binomial variable:
where is the Beta function.
From these values, we find the posterior probability of which strongly favors over .
The two approaches—the Bayesian and the frequentist—appear to be in conflict, and this is the "paradox".
Reconciling the Bayesian and frequentist approaches
Naaman[3] proposed an adaption of the significance level to the sample size in order to control false positives: Template:Math, such that Template:Math with Template:Math. At least in the numerical example, taking Template:Math, results in a significance level of 0.00318, so the frequentist would not reject the null hypothesis, which is in agreement with the Bayesian approach.
Uninformative priors
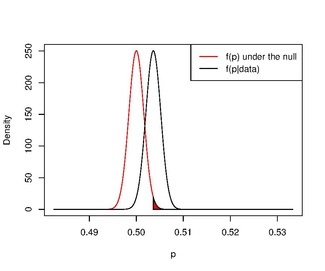
If we use an uninformative prior and test a hypothesis more similar to that in the frequentist approach, the paradox disappears.
For example, if we calculate the posterior distribution , using a uniform prior distribution on (i.e. ), we find
If we use this to check the probability that a newborn is more likely to be a boy than a girl, i.e. we find
In other words, it is very likely that the proportion of male births is above 0.5.
Neither analysis gives an estimate of the effect size, directly, but both could be used to determine, for instance, if the fraction of boy births is likely to be above some particular threshold.
The lack of an actual paradox
Template:No footnotes The apparent disagreement between the two approaches is caused by a combination of factors. First, the frequentist approach above tests without reference to . The Bayesian approach evaluates as an alternative to and finds the first to be in better agreement with the observations. This is because the latter hypothesis is much more diffuse, as can be anywhere in , which results in it having a very low posterior probability. To understand why, it is helpful to consider the two hypotheses as generators of the observations:
- Under , we choose and ask how likely it is to see Template:Val boys in Template:Val births.
- Under , we choose randomly from anywhere within 0 to 1 and ask the same question.
Most of the possible values for under are very poorly supported by the observations. In essence, the apparent disagreement between the methods is not a disagreement at all, but rather two different statements about how the hypotheses relate to the data:
- The frequentist finds that is a poor explanation for the observation.
- The Bayesian finds that is a far better explanation for the observation than
The ratio of the sex of newborns is improbably 50/50 male/female, according to the frequentist test. Yet 50/50 is a better approximation than most, but not all, other ratios. The hypothesis would have fit the observation much better than almost all other ratios, including
For example, this choice of hypotheses and prior probabilities implies the statement "if > 0.49 and < 0.51, then the prior probability of being exactly 0.5 is 0.50/0.51 ≈ 98%". Given such a strong preference for it is easy to see why the Bayesian approach favors in the face of even though the observed value of lies away from 0.5. The deviation of over 2σ from is considered significant in the frequentist approach, but its significance is overruled by the prior in the Bayesian approach.
Looking at it another way, we can see that the prior distribution is essentially flat with a delta function at Clearly, this is dubious. In fact, picturing real numbers as being continuous, it would be more logical to assume that it would be impossible for any given number to be exactly the parameter value, i.e., we should assume
A more realistic distribution for in the alternative hypothesis produces a less surprising result for the posterior of For example, if we replace with i.e., the maximum likelihood estimate for the posterior probability of would be only 0.07 compared to 0.93 for (of course, one cannot actually use the MLE as part of a prior distribution).