Circulant graph
Template:Short description Template:For
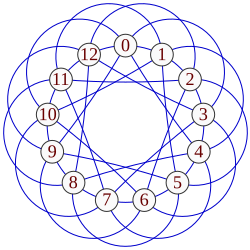
In graph theory, a circulant graph is an undirected graph acted on by a cyclic group of symmetries which takes any vertex to any other vertex. It is sometimes called a cyclic graph,[1] but this term has other meanings.
Equivalent definitions
Circulant graphs can be described in several equivalent ways:[2]
- The automorphism group of the graph includes a cyclic subgroup that acts transitively on the graph's vertices. In other words, the graph has an automorphism which is a cyclic permutation of its vertices.
- The graph has an adjacency matrix that is a circulant matrix.
- The Template:Mvar vertices of the graph can be numbered from 0 to Template:Math in such a way that, if some two vertices numbered Template:Mvar and Template:Math are adjacent, then every two vertices numbered Template:Mvar and Template:Math are adjacent.
- The graph can be drawn (possibly with crossings) so that its vertices lie on the corners of a regular polygon, and every rotational symmetry of the polygon is also a symmetry of the drawing.
- The graph is a Cayley graph of a cyclic group.[3]
Examples
Every cycle graph is a circulant graph, as is every crown graph with number of vertices congruent to 2 modulo 4.
The Paley graphs of order Template:Mvar (where Template:Mvar is a prime number congruent to Template:Nowrap) is a graph in which the vertices are the numbers from 0 to Template:Math and two vertices are adjacent if their difference is a quadratic residue modulo Template:Mvar. Since the presence or absence of an edge depends only on the difference modulo Template:Mvar of two vertex numbers, any Paley graph is a circulant graph.
Every Möbius ladder is a circulant graph, as is every complete graph. A complete bipartite graph is a circulant graph if it has the same number of vertices on both sides of its bipartition.
If two numbers Template:Mvar and Template:Mvar are relatively prime, then the Template:Math rook's graph (a graph that has a vertex for each square of an Template:Math chessboard and an edge for each two squares that a rook can move between in a single move) is a circulant graph. This is because its symmetries include as a subgroup the cyclic group Cmn Cm×Cn. More generally, in this case, the tensor product of graphs between any Template:Mvar- and Template:Mvar-vertex circulants is itself a circulant.[2]
Many of the known lower bounds on Ramsey numbers come from examples of circulant graphs that have small maximum cliques and small maximum independent sets.[1]
A specific example
The circulant graph with jumps is defined as the graph with nodes labeled where each node i is adjacent to 2k nodes .
- The graph is connected if and only if .
- If are fixed integers then the number of spanning trees where satisfies a recurrence relation of order .
- In particular, where is the n-th Fibonacci number.
Self-complementary circulants
A self-complementary graph is a graph in which replacing every edge by a non-edge and vice versa produces an isomorphic graph. For instance, a five-vertex cycle graph is self-complementary, and is also a circulant graph. More generally every Paley graph of prime order is a self-complementary circulant graph.[4] Horst Sachs showed that, if a number Template:Mvar has the property that every prime factor of Template:Mvar is congruent to Template:Nowrap, then there exists a self-complementary circulant with Template:Mvar vertices. He conjectured that this condition is also necessary: that no other values of Template:Mvar allow a self-complementary circulant to exist.[2][4] The conjecture was proven some 40 years later, by Vilfred.[2]
Ádám's conjecture
Define a circulant numbering of a circulant graph to be a labeling of the vertices of the graph by the numbers from 0 to Template:Math in such a way that, if some two vertices numbered Template:Mvar and Template:Mvar are adjacent, then every two vertices numbered Template:Mvar and Template:Math are adjacent. Equivalently, a circulant numbering is a numbering of the vertices for which the adjacency matrix of the graph is a circulant matrix.
Let Template:Mvar be an integer that is relatively prime to Template:Mvar, and let Template:Mvar be any integer. Then the linear function that takes a number Template:Mvar to Template:Math transforms a circulant numbering to another circulant numbering. András Ádám conjectured that these linear maps are the only ways of renumbering a circulant graph while preserving the circulant property: that is, if Template:Mvar and Template:Mvar are isomorphic circulant graphs, with different numberings, then there is a linear map that transforms the numbering for Template:Mvar into the numbering for Template:Mvar. However, Ádám's conjecture is now known to be false. A counterexample is given by graphs Template:Mvar and Template:Mvar with 16 vertices each; a vertex Template:Mvar in Template:Mvar is connected to the six neighbors Template:Math, Template:Math, and Template:Math modulo 16, while in Template:Mvar the six neighbors are Template:Math, Template:Math, and Template:Math modulo 16. These two graphs are isomorphic, but their isomorphism cannot be realized by a linear map.[2]
Toida's conjecture refines Ádám's conjecture by considering only a special class of circulant graphs, in which all of the differences between adjacent graph vertices are relatively prime to the number of vertices. According to this refined conjecture, these special circulant graphs should have the property that all of their symmetries come from symmetries of the underlying additive group of numbers modulo Template:Math. It was proven by two groups in 2001 and 2002.[5][6]
Algorithmic questions
There is a polynomial-time recognition algorithm for circulant graphs, and the isomorphism problem for circulant graphs can be solved in polynomial time.[7][8]
References
External links
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Small Ramsey Numbers, Stanisław P. Radziszowski, Electronic J. Combinatorics, dynamic survey 1, updated 2014.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Template:Citation.
- ↑ Template:Citation.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Template:Cite journal.
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Citation
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite journal