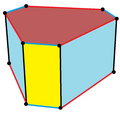
Hexagonal prism
Template:Short description Template:Prism polyhedra db File:Prisma hexagonal 3D.stl
In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. Prisms are polyhedrons; this polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices.[1]
Since it has 8 faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term octahedron is primarily used to refer to the regular octahedron, which has eight triangular faces. Because of the ambiguity of the term octahedron and tilarity of the various eight-sided figures, the term is rarely used without clarification.
Before sharpening, many pencils take the shape of a long hexagonal prism.[2]
As a semiregular (or uniform) polyhedron
If faces are all regular, the hexagonal prism is a semiregular polyhedron, more generally, a uniform polyhedron, and the fourth in an infinite set of prisms formed by square sides and two regular polygon caps. It can be seen as a truncated hexagonal hosohedron, represented by Schläfli symbol t{2,6}. Alternately it can be seen as the Cartesian product of a regular hexagon and a line segment, and represented by the product {6}×{}. The dual of a hexagonal prism is a hexagonal bipyramid.
The symmetry group of a right hexagonal prism is D6h of order 24. The rotation group is D6 of order 12.
Volume
As in most prisms, the volume is found by taking the area of the base, with a side length of , and multiplying it by the height , giving the formula:[3]
and its surface area can be .
Symmetry
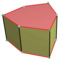
The topology of a uniform hexagonal prism can have geometric variations of lower symmetry, including:
| Name | Regular-hexagonal prism | Hexagonal frustum | Ditrigonal prism | Triambic prism | Ditrigonal trapezoprism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | D6h, [2,6], (*622) | C6v, [6], (*66) | D3h, [2,3], (*322) | D3d, [2+,6], (2*3) | |
| Construction | {6}×{}, Template:CDD | t{3}×{}, Template:CDD | Template:CDD | s2{2,6}, Template:CDD | |
| Image | 
|

|

|

| |
| Distortion | 
|
|
|

| |
As part of spatial tesselations
It exists as cells of four prismatic uniform convex honeycombs in 3 dimensions:
It also exists as cells of a number of four-dimensional uniform 4-polytopes, including:
Related polyhedra and tilings
Template:Hexagonal dihedral truncations
This polyhedron can be considered a member of a sequence of uniform patterns with vertex figure (4.6.2p) and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram Template:CDD. For p < 6, the members of the sequence are omnitruncated polyhedra (zonohedrons), shown below as spherical tilings. For p > 6, they are tilings of the hyperbolic plane, starting with the truncated triheptagonal tiling.
See also
References
External links
- Uniform Honeycombs in 3-Space VRML models
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra Prisms and antiprisms
- Template:Mathworld
- Hexagonal Prism Interactive Model -- works in your web browser